Parallel programming in .NET - Introduction
What is parallel programming?
Sequential programming assumes a set of instructions that are executed sequentially by a single processor. The point of parallel programming is to program systems that consist of multiple processors and therefore have multiple simultaneous instruction streams.
Why do we need it?
The clock speeds of chips are no longer increasing. All future improvements in computer speed will come from parallelism. In other words, more and more processors are being added to new computers. These chips enable software to do multiple tasks at the same time. Each processor its own task. So one way to make applications run faster, is to use parallel programming. This is not the same as multithreading, though. Multithreading can be done on a single core CPU. In that case, two threads can never execute at the same time on the CPU. The operating system (which takes care of multi-threading) divides the time of the processor between all open threads. When you have too many executing threads at once, your system slows down as there is not enough time for all the threads to run at full speed.
Concurrent vs Parallel
To be clear, parallel programming is not the same as concurrent programming. As they say, a picture says more than a thousand words:
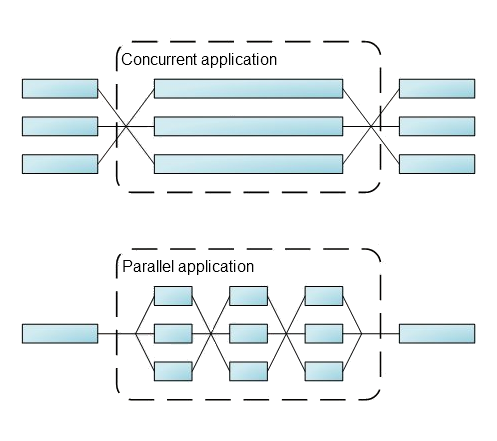
Well, maybe it could use some explanation.
- Concurrent applications tend to create a thread that handles a whole series of tasks. Most of the time these concurrent applications create threads because they need an isolated process for a concurrent event.
- Parallel applications divide a process into small tasks that are executed on seperate threads. Because the tasks are small, the threads can be divided evenly over the processors, resulting in very efficient use of a multi-core CPU.
Parallel programming in .NET 4.0
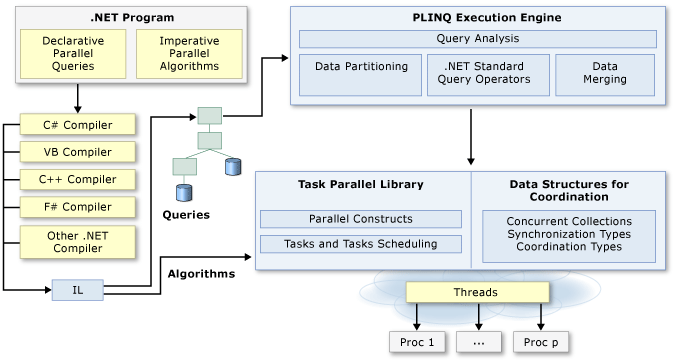
In the .NET 4.0 framework parallel is included in the form of Task Parallel Library (TPL) and Parallel LINQ (PLINQ). These functions are actually built on top of the existing thread pool in previous versions of the .NET framework. Parallel is pretty easy to implement, but also very easy to misuse or overuse. Caution is required!
Resources
The following resources provide an introduction to parallel programming in C# 4.0 and provide some guidelines and best practices: